Introduction:
Sports have long been a significant aspect of human culture, providing entertainment, promoting physical activity, and fostering community spirit. However, the impact of sports extends far beyond the playing field, with a profound influence on the global economy. This article delves into the multifaceted effects of sports on the economy, exploring their role in job creation, revenue generation, infrastructure development, tourism, and social development.
Job Creation:
The sports industry is a significant employer, providing jobs for millions of people worldwide. From professional athletes and coaches to stadium staff, sports equipment manufacturers, and media personnel, the industry supports a vast workforce. According to the International Labour Organization, the sports industry generates over 20 million jobs globally, contributing significantly to national economies.
Revenue Generation:
Sports are a lucrative business, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year. Professional leagues, tournaments, and events attract massive audiences, driving ticket sales, merchandise, and broadcasting rights. The global sports market is projected to reach $73.7 billion by 2025, with the NFL, NBA, MLB, and Premier League among the top-grossing leagues.
Infrastructure Development:
Major sporting events like the Olympics, World Cup, and Commonwealth Games drive infrastructure development, as host cities invest in stadiums, arenas, and transportation systems. These projects create construction jobs, stimulate local economies, and leave a lasting legacy for the community.
Tourism:
Sports tourism is a growing sector, with fans traveling to attend events, visit iconic stadiums, and experience the culture of host cities. According to the World Tourism Organization, sports tourism generates over $600 billion annually, supporting local businesses and contributing to national economies.
Social Development:
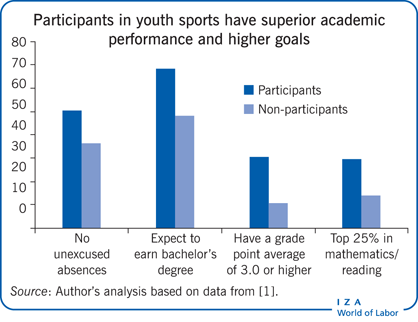
Sports have a profound impact on social development, promoting health, education, and social cohesion. Participating in sports improves physical and mental health, while also teaching valuable life skills like teamwork, discipline, and perseverance. Sports programs in underprivileged communities provide a positive outlet for youth, reducing crime and improving academic performance.
Conclusion:
The impact of sports on the global economy is profound, driving job creation, revenue generation, infrastructure development, tourism, and social development. As the sports industry continues to grow, its influence on the economy will only increase, shaping the future of nations and communities worldwide.