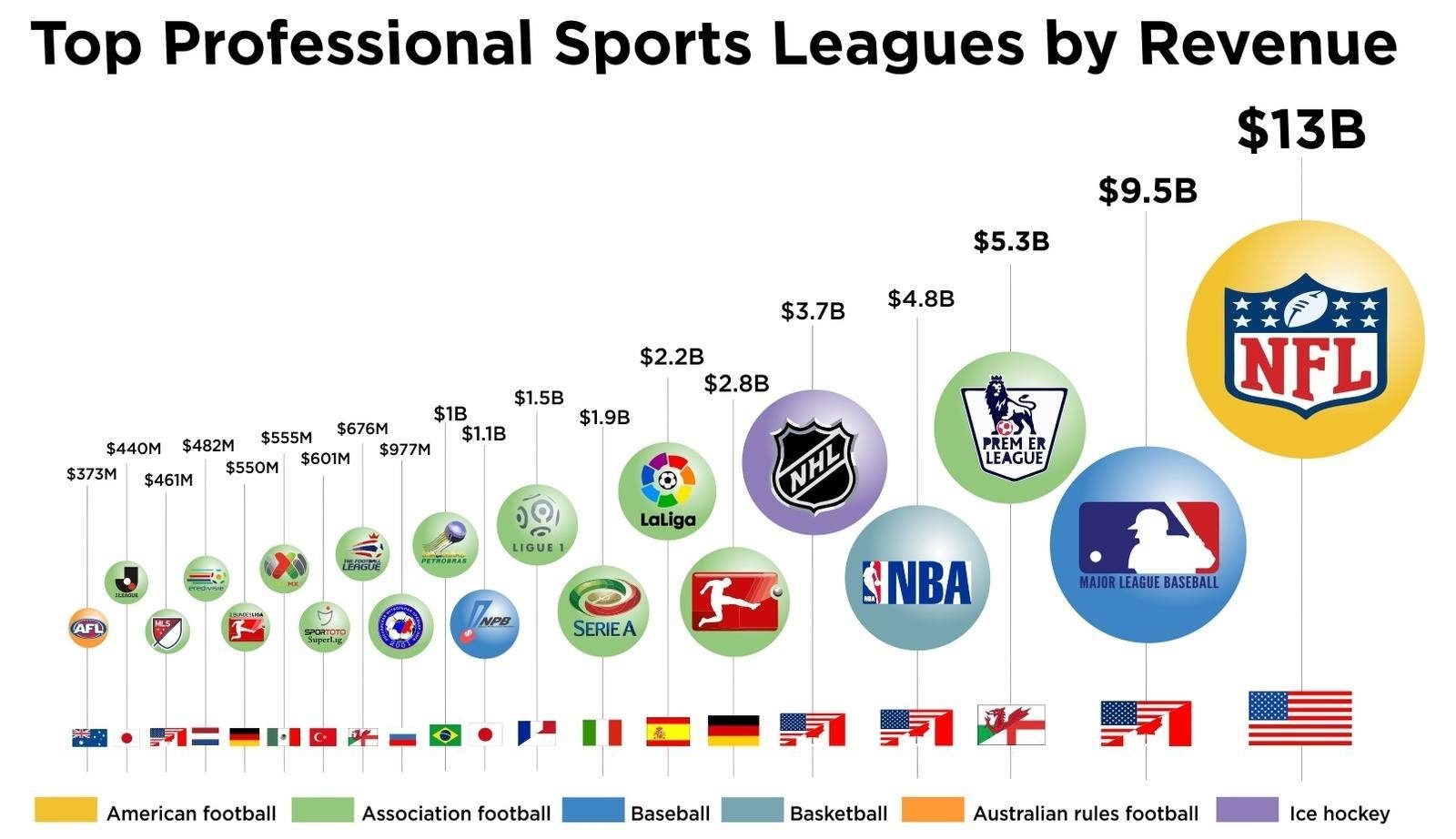
Introduction
Sports is a multi-billion-dollar industry, with professional teams and leagues generating revenue through a variety of channels. From ticket sales and sponsorships to merchandise and media rights, the business of sports is complex and fascinating. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of sports finance, exploring how teams and leagues make money, and the key drivers of their revenue.
Revenue Streams
- Ticket Sales
Ticket sales are a significant source of revenue for sports teams. Teams generate revenue from season ticket sales, individual game tickets, and premium seating options like suites and club seats.
- Sponsorships and Partnerships
Sponsorships and partnerships with brands are a crucial revenue stream for teams and leagues. These deals can include jersey sponsorships, stadium naming rights, and official partnerships.
- Media Rights
Media rights deals are a major source of revenue for sports leagues and teams. These deals include television contracts, streaming rights, and radio broadcasts.
- Merchandise
Merchandise sales, including jerseys, hats, and other team-branded items, generate significant revenue for teams and leagues.
- Licensing
Licensing agreements allow teams and leagues to earn revenue from the use of their intellectual property, such as logos and trademarks.
- Stadium and Arena Revenue
Stadium and arena revenue includes concessions, parking, and other event-related income.
- Digital Revenue
Digital revenue streams include online ticket sales, digital sponsorships, and e-commerce sales.
Team Ownership and Financing
- Private Ownership
Many sports teams are privately owned by individuals or families, who finance the team through personal wealth or investment.
- Public Ownership
Some teams are publicly owned, with fans and investors holding shares in the team.
- Debt Financing
Teams may use debt financing to fund operations, renovations, or new stadium construction.
League Revenue Sharing
- National Football League (NFL)
The NFL has a robust revenue-sharing model, distributing television revenue, sponsorships, and other income equally among teams.
- National Basketball Association (NBA)
The NBA also has a revenue-sharing model, distributing television revenue, sponsorships, and other income based on team performance and market size.
- Major League Baseball (MLB)
MLB has a more complex revenue-sharing model, with teams receiving a percentage of revenue based on market size, attendance, and other factors.
Marketing and Branding
- Social Media
Teams and leagues leverage social media to engage with fans, promote their brand, and drive revenue.
- Brand Partnerships
Teams and leagues partner with brands to create co-branded marketing campaigns and promotions.
- Fan Engagement
Teams and leagues focus on enhancing the fan experience, including in-stadium entertainment, promotions, and loyalty programs.
Conclusion
The business of sports is a complex and multifaceted industry, with teams and leagues generating revenue through various channels. Understanding these revenue streams, financing models, and marketing strategies is essential for teams and leagues to succeed in the competitive world of sports. As the industry continues to evolve, we can expect new revenue streams and innovations to emerge, further driving the growth of the sports business.